What is a catalytic converter and how does it work?
A catalytic converter is a device that uses a catalyst to convert three harmful compounds in car exhaust into harmless compounds.
The three harmful compounds are:- Hydrocarbons (in the form of unburned gasoline)
- Carbon monoxide (formed by the combustion of gasoline)
- Nitrogen oxides (created when the heat in the engine forces nitrogen in the air to combine with oxygen)
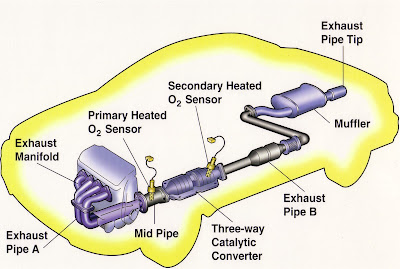
In a catalytic converter, the catalyst (in the form of platinum and palladium) is coated onto a ceramic honeycomb or ceramic beads that are housed in a muffler-like package attached to the exhaust pipe. The catalyst helps to convert carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. It converts the hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water. It also converts the nitrogen oxides back into nitrogen and oxygen.
Most commonly used in an automobile's exhaust system, catalytic converters are now commonly used on generator sets, forklifts, mining equipment, trucks, buses, trains, and other machines that have engines to provide an environment for a chemical reaction where unburned hydrocarbons are more completely combusted.
Catalytic converters are still most commonly used in exhaust systems in automobiles, but are also used on generator sets, forklifts, mining equipment, trucks, buses, locomotives, motorcycles, airplanes and other engine-fitted devices.
Types
Two-way
A two-way (or "oxidation") catalytic converter has two simultaneous tasks:- Oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide: 2CO + O2 → 2CO2
- Oxidation of hydrocarbons (unburnt and partially burnt fuel) to carbon dioxide and water: CxH2x+2 + [(3x+1)/2] O2 → xCO2 + (x+1) H2O (a combustion reaction)
Three-way
Since 1981, "three-way" (oxidation-reduction) catalytic converters have been used in vehicle emission control systems in the United States and Canada; many other countries have also adopted stringent vehicle emission regulations that in effect require three-way converters on gasoline-powered vehicles. The reduction and oxidation catalysts are typically contained in a common housing, however in some instances they may be housed separately. A three-way catalytic converter has three simultaneous tasks:- Reduction of nitrogen oxides to nitrogen and oxygen: 2NOx → xO2 + N2
- Oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide: 2CO + O2 → 2CO2
- Oxidation of unburnt hydrocarbons (HC) to carbon dioxide and water: CxH2x+2 + [(3x+1)/2]O2 → xCO2 + (x+1)H2O.
No comments:
Post a Comment